Xanthan Gum: A Versatile Tool in Pharmaceutical Formulation
Related Articles: Xanthan Gum: A Versatile Tool in Pharmaceutical Formulation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Xanthan Gum: A Versatile Tool in Pharmaceutical Formulation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Xanthan Gum: A Versatile Tool in Pharmaceutical Formulation

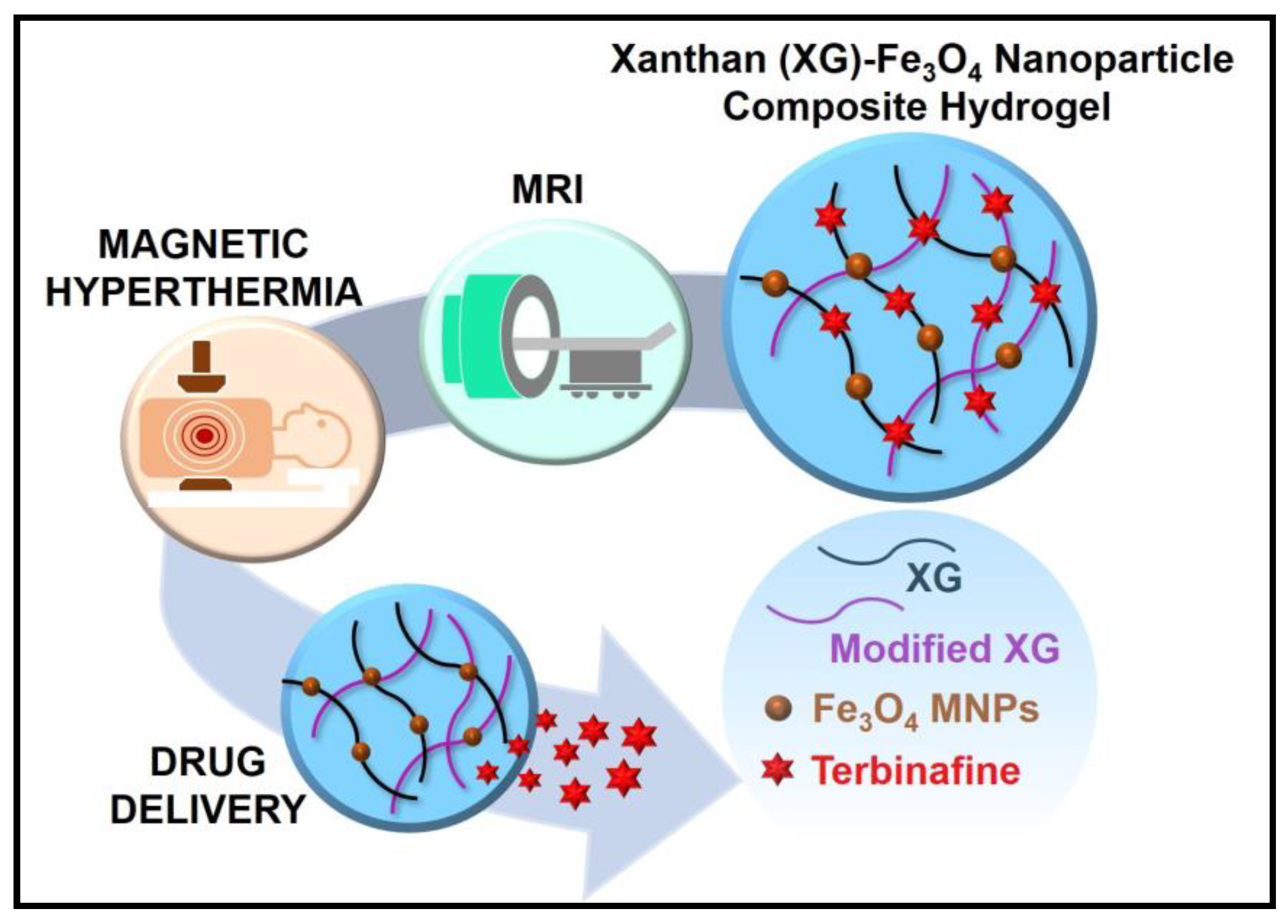
Xanthan gum, a natural polysaccharide produced through the fermentation of carbohydrates by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris, has found a significant niche in the pharmaceutical industry. Its unique properties, including its ability to thicken, stabilize, and modify the viscosity of liquids, have made it an invaluable ingredient in a wide range of pharmaceutical formulations. This article explores the diverse applications of xanthan gum in pharmaceuticals, highlighting its critical role in enhancing drug delivery, improving product stability, and ultimately, contributing to patient well-being.
Understanding the Properties of Xanthan Gum
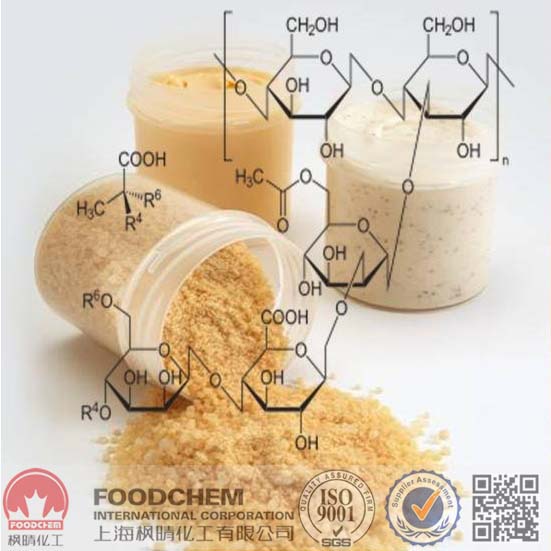
Xanthan gum’s versatility stems from its molecular structure. It comprises a linear backbone of glucose units, with side chains of mannose and glucuronic acid. This structure, along with its ability to form a viscous solution at low concentrations, contributes to its key properties:
- Viscosity Enhancement: Xanthan gum significantly increases the viscosity of liquids, forming a thick, gel-like consistency. This property is crucial for creating suspensions, emulsions, and other dosage forms that require controlled release and improved stability.
- Suspension Stabilization: Its ability to form a viscous matrix helps to keep solid particles suspended in liquid formulations, preventing sedimentation and ensuring uniform drug distribution.
- Emulsion Stabilization: Xanthan gum acts as an emulsifier, stabilizing the interface between oil and water phases in emulsions. This property is essential for producing stable and homogenous formulations.
- Biocompatibility and Safety: Xanthan gum is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for use in food and pharmaceutical applications. It is well-tolerated by the human body and exhibits minimal toxicity.
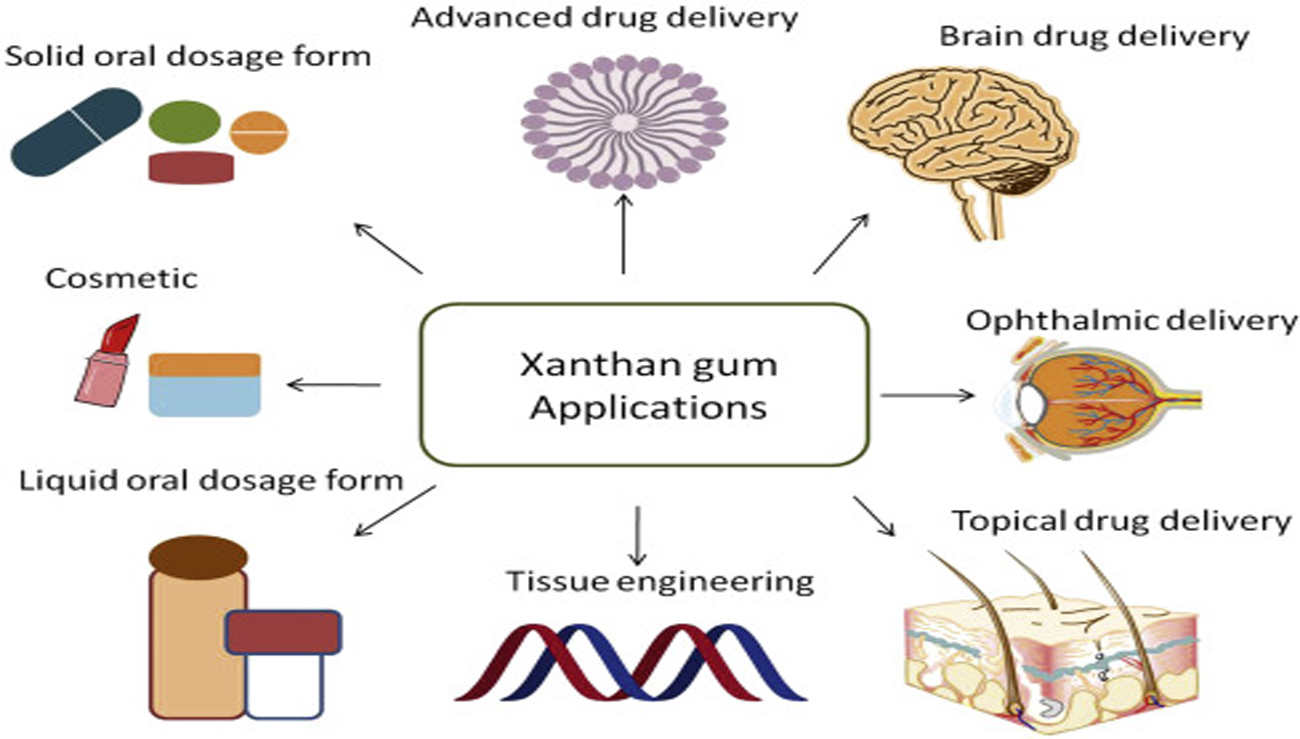
Applications of Xanthan Gum in Pharmaceutical Formulations
The versatility of xanthan gum has led to its widespread use in various pharmaceutical formulations, impacting both oral and topical drug delivery:
1. Oral Solid Dosage Forms:
- Tablets and Capsules: Xanthan gum can improve the flowability and compressibility of powders, facilitating the production of uniform tablets and capsules.
- Granules: Xanthan gum helps to bind granules together, improving their stability and reducing dust formation during handling and packaging.
- Controlled Release Formulations: Xanthan gum’s ability to form a viscous matrix can be utilized to create controlled-release formulations. It slows down the dissolution and absorption of drugs, extending their duration of action and improving patient compliance.
2. Oral Liquid Dosage Forms:
- Suspensions: Xanthan gum is a key ingredient in oral suspensions, providing the viscosity necessary to keep solid drug particles evenly dispersed. This ensures consistent dosing and prevents sedimentation.
- Emulsions: Xanthan gum stabilizes oil-in-water emulsions, ensuring homogenous distribution of the active ingredients and improving the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
- Syrups and Elixirs: Xanthan gum contributes to the viscosity and texture of syrups and elixirs, making them easier to swallow and improving their palatability.
3. Topical Formulations:
- Creams and Lotions: Xanthan gum enhances the viscosity and spreadability of creams and lotions, improving their texture and feel on the skin.
- Ointments: It acts as a thickening agent in ointments, improving their consistency and adherence to the skin.
- Gels: Xanthan gum is used to create gels that can deliver drugs transdermally, enhancing their absorption and efficacy.
4. Parenteral Formulations:
- Injectable Suspensions: Xanthan gum can be used to stabilize injectable suspensions, ensuring uniform distribution of the drug and preventing particle aggregation.
- Microemulsions: Xanthan gum contributes to the formation and stability of microemulsions, enabling the efficient delivery of poorly soluble drugs intravenously.
5. Other Applications:
- Bioadhesive Formulations: Xanthan gum’s ability to form a viscous gel can be harnessed to create bioadhesive formulations that adhere to mucosal surfaces, prolonging drug residence time and enhancing absorption.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Xanthan gum can be incorporated into novel drug delivery systems, such as microspheres and nanoparticles, to improve drug targeting, controlled release, and bioavailability.
Benefits of Using Xanthan Gum in Pharmaceuticals
The use of xanthan gum in pharmaceuticals offers several advantages:
- Improved Drug Delivery: It enhances the stability and uniformity of formulations, ensuring consistent drug delivery and maximizing bioavailability.
- Enhanced Patient Compliance: Xanthan gum contributes to the palatability and ease of administration of oral formulations, improving patient compliance.
- Extended Drug Action: Its ability to control drug release can extend the duration of action of medications, reducing the frequency of dosing and improving patient convenience.
- Reduced Side Effects: By controlling the release of drugs, xanthan gum can minimize the risk of peak plasma concentrations and associated side effects.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Xanthan gum is a relatively inexpensive ingredient, making it a cost-effective solution for improving the quality and efficacy of pharmaceutical formulations.
FAQs on Xanthan Gum in Pharmaceuticals
1. Is Xanthan Gum Safe for Use in Pharmaceuticals?
Yes, xanthan gum is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for use in food and pharmaceutical applications. It is well-tolerated by the human body and exhibits minimal toxicity.
2. What are the Potential Side Effects of Xanthan Gum?
Xanthan gum is generally well-tolerated. However, some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal side effects, such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. These side effects are usually mild and transient.
3. Can Xanthan Gum Interact with Other Medications?
While xanthan gum is generally considered safe, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss any potential interactions with other medications.
4. How is Xanthan Gum Produced?
Xanthan gum is produced through the fermentation of carbohydrates by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. The bacteria are grown in a medium containing sugars, such as corn starch or glucose. The resulting polysaccharide is then purified and dried to produce xanthan gum powder.
5. Where Can I Find Xanthan Gum?
Xanthan gum is widely available as a pharmaceutical-grade ingredient from various suppliers. It can be purchased in powder form or as a pre-mixed solution.
Tips for Using Xanthan Gum in Pharmaceuticals
- Start with a Low Concentration: Begin with a low concentration of xanthan gum and gradually increase it until the desired viscosity is achieved.
- Proper Hydration: Ensure proper hydration of xanthan gum by slowly adding it to water or other liquids while stirring continuously.
- Temperature Control: Xanthan gum is sensitive to temperature changes. It is best to use it at room temperature or slightly above.
- Compatibility Testing: Conduct compatibility testing with other ingredients in the formulation to ensure that xanthan gum does not affect their stability or efficacy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the xanthan gum used meets all relevant regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical applications.
Conclusion
Xanthan gum has become an indispensable tool in the pharmaceutical industry, contributing significantly to the development of safe, effective, and patient-friendly formulations. Its unique properties, including its ability to enhance viscosity, stabilize suspensions and emulsions, and control drug release, have made it a valuable ingredient in a wide range of dosage forms. As research and development in the pharmaceutical industry continues to advance, xanthan gum’s versatility and safety profile position it for continued use in innovative drug delivery systems and novel therapies.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Xanthan Gum: A Versatile Tool in Pharmaceutical Formulation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!