The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet
Related Articles: The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet
- 3.1 The Nutritional Powerhouse of Produce
- 3.2 The Health Benefits of Consuming Produce
- 3.3 Tips for Maximizing Produce Consumption
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions about Produce
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet

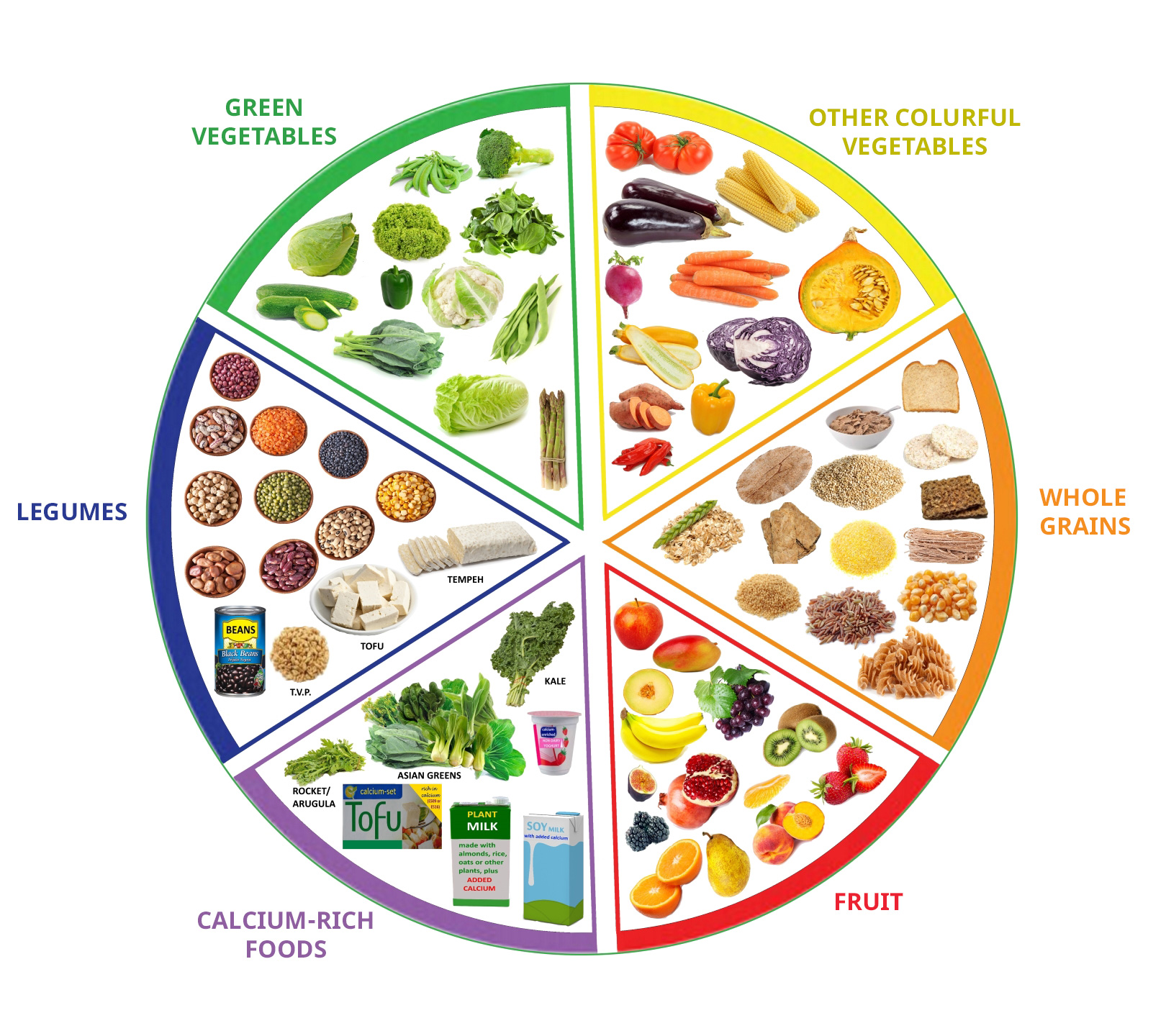
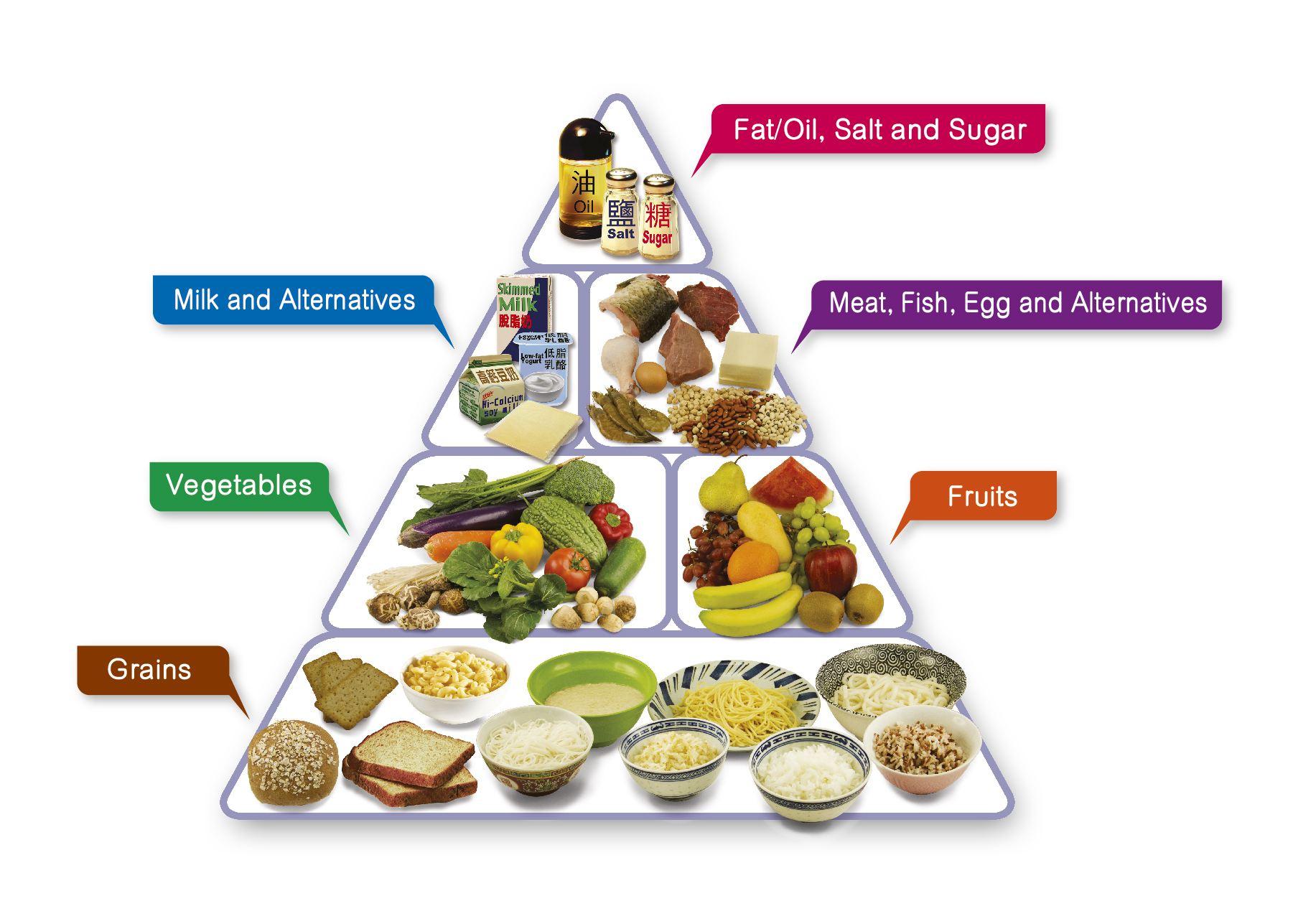
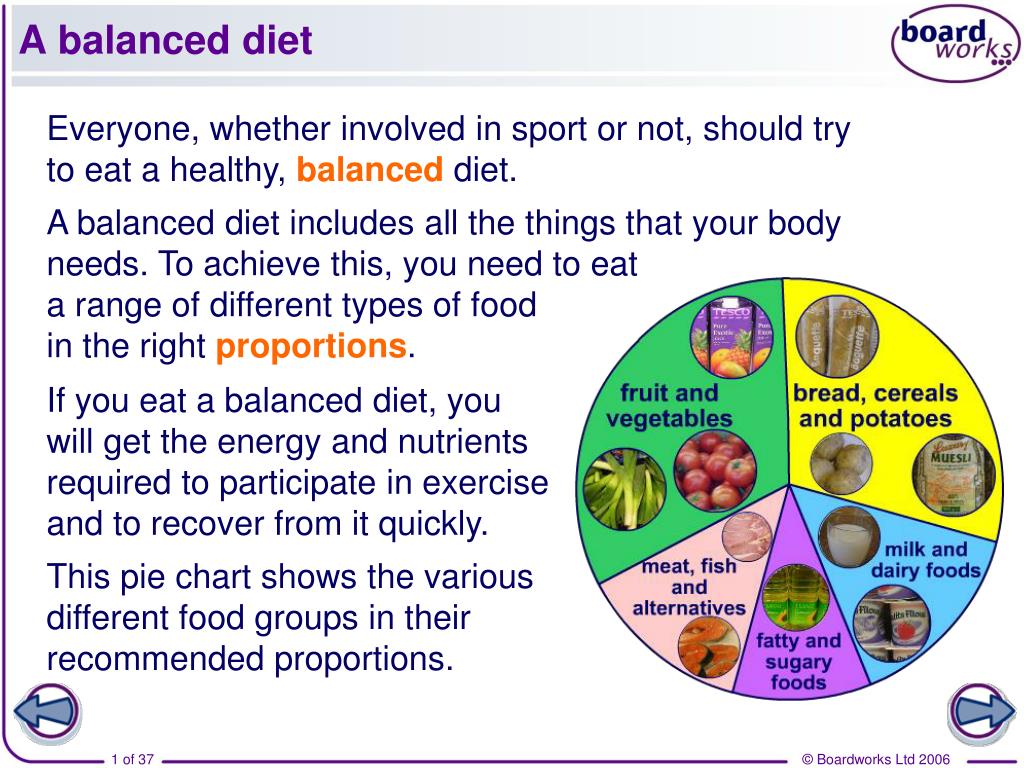
The term "produce" encompasses a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and legumes that are essential components of a healthy diet. These foods provide a wealth of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that are crucial for optimal physical and mental well-being. This article delves into the significance of incorporating produce into one’s daily meals, exploring its multifaceted benefits and providing practical tips for maximizing its consumption.
The Nutritional Powerhouse of Produce
Produce is renowned for its exceptional nutritional profile, offering a diverse array of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are vital for maintaining overall health.
Vitamins:
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that supports immune function, collagen production, and wound healing. Found abundantly in citrus fruits, berries, and leafy green vegetables.
- Vitamin A: Crucial for vision, skin health, and immune function. Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health. Found in leafy green vegetables like kale, spinach, and collard greens.
- Folate: Vital for cell growth and development, particularly important during pregnancy. Found in leafy green vegetables, asparagus, and legumes.
Minerals:
- Potassium: Plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure, muscle function, and nerve transmission. Found in bananas, avocados, potatoes, and leafy green vegetables.
- Magnesium: Essential for muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and bone health. Found in leafy green vegetables, almonds, avocado, and dark chocolate.
- Calcium: Crucial for strong bones and teeth, muscle function, and nerve transmission. Found in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods.
- Iron: Essential for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Found in red meat, beans, lentils, and leafy green vegetables.
Antioxidants:
Produce is rich in antioxidants, which protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Fiber:
Produce is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
The Health Benefits of Consuming Produce
Incorporating a variety of produce into one’s diet offers a wide range of health benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables is linked to a lower risk of developing heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and other chronic conditions.
- Improved digestive health: Fiber-rich produce promotes regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
- Enhanced immune function: Vitamins C and A, abundant in produce, strengthen the immune system, making it more resilient to infections and illnesses.
- Improved blood pressure control: Potassium-rich produce helps regulate blood pressure, reducing the risk of hypertension.
- Weight management: High in fiber and low in calories, produce promotes satiety and helps manage weight effectively.
- Improved skin health: Antioxidants in produce protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, promoting a youthful and healthy complexion.
Tips for Maximizing Produce Consumption
- Variety is key: Choose a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and legumes to ensure a diverse intake of nutrients.
- Incorporate produce into every meal: Include fruits and vegetables in breakfast, lunch, and dinner, as well as snacks.
- Prepare produce in various ways: Experiment with different cooking methods such as steaming, roasting, grilling, and stir-frying to enhance flavor and maintain nutrients.
- Store produce properly: Refrigerate fruits and vegetables to preserve their freshness and quality.
- Plan meals ahead: Having a meal plan in place can make it easier to incorporate produce into your diet.
- Grow your own produce: Gardening can be a rewarding way to ensure access to fresh, homegrown produce.
Frequently Asked Questions about Produce
Q: How much produce should I eat daily?
A: The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend consuming at least 2.5 cups of vegetables and 2 cups of fruit per day for a 2,000-calorie diet.
Q: What are the best sources of specific nutrients in produce?
A: Refer to reliable sources like the USDA Food Composition Database for detailed information on the nutrient content of various fruits and vegetables.
Q: How can I ensure I’m getting enough nutrients from produce?
A: Consume a variety of produce daily, including both raw and cooked options. Consider supplementing with a multivitamin if you are concerned about nutrient deficiencies.
Q: Is organic produce always better?
A: Organic produce is grown without the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which may be a preference for some consumers. However, conventional produce is also safe for consumption, and the difference in nutrient content is often minimal.
Q: What are the best ways to store produce to maximize freshness?
A: Store fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator, separated by type, and avoid storing them near ethylene-producing fruits like bananas and apples, which can cause other produce to ripen faster.
Conclusion
Incorporating a variety of produce into one’s daily diet is paramount for maintaining optimal health and well-being. The rich nutritional profile of fruits, vegetables, and legumes provides a wide range of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, promoting overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and supporting a balanced lifestyle. By embracing the abundance and diversity of produce available, individuals can empower themselves with the tools necessary to achieve a healthier and more vibrant life.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Vital Role of Produce in a Balanced Diet. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!