The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Pathways
Related Articles: The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Pathways
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Pathways. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Pathways

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, is more than just unsightly blemishes. It is a multifaceted issue rooted in a complex interplay of factors, both internal and external. While often perceived as a teenage problem, acne can persist well into adulthood, significantly impacting self-esteem and quality of life. This article delves into the diverse factors that contribute to acne development, offering a comprehensive understanding of its underlying mechanisms.
The Role of Hormones:
Hormonal fluctuations play a pivotal role in acne development, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy. Androgens, primarily testosterone, stimulate sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the skin. Increased androgen levels, common during these periods, lead to excessive sebum production, clogging hair follicles and creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
The Importance of Genetics:
Family history plays a significant role in acne susceptibility. Individuals with a genetic predisposition are more likely to develop acne due to inherited traits influencing sebum production, follicular structure, and inflammatory responses. While genetics cannot be altered, understanding its influence can help individuals adopt proactive strategies for managing acne.
The Impact of Diet:
While the direct link between diet and acne remains a subject of ongoing research, certain dietary factors can contribute to its severity. High-glycemic index (GI) foods, such as sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates, can trigger an inflammatory response, potentially exacerbating acne. Conversely, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to improved skin health.
The Influence of Stress:
Stress, a common aspect of modern life, can significantly impact acne. Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can increase sebum production, leading to clogged pores and inflammation. Moreover, stress can disrupt sleep patterns, further contributing to hormonal imbalances and exacerbating acne.
The Role of Bacteria:
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a common bacterium residing on the skin, plays a crucial role in acne development. When sebum clogs hair follicles, it creates an anaerobic environment where P. acnes thrives. The bacteria then release inflammatory substances, triggering an immune response that leads to redness, swelling, and pustules.
The Impact of Environmental Factors:
External factors can also influence acne. Pollution, humidity, and excessive heat can contribute to clogged pores and inflammation. Certain cosmetics and skincare products, particularly those containing comedogenic ingredients (ingredients that clog pores), can exacerbate acne.
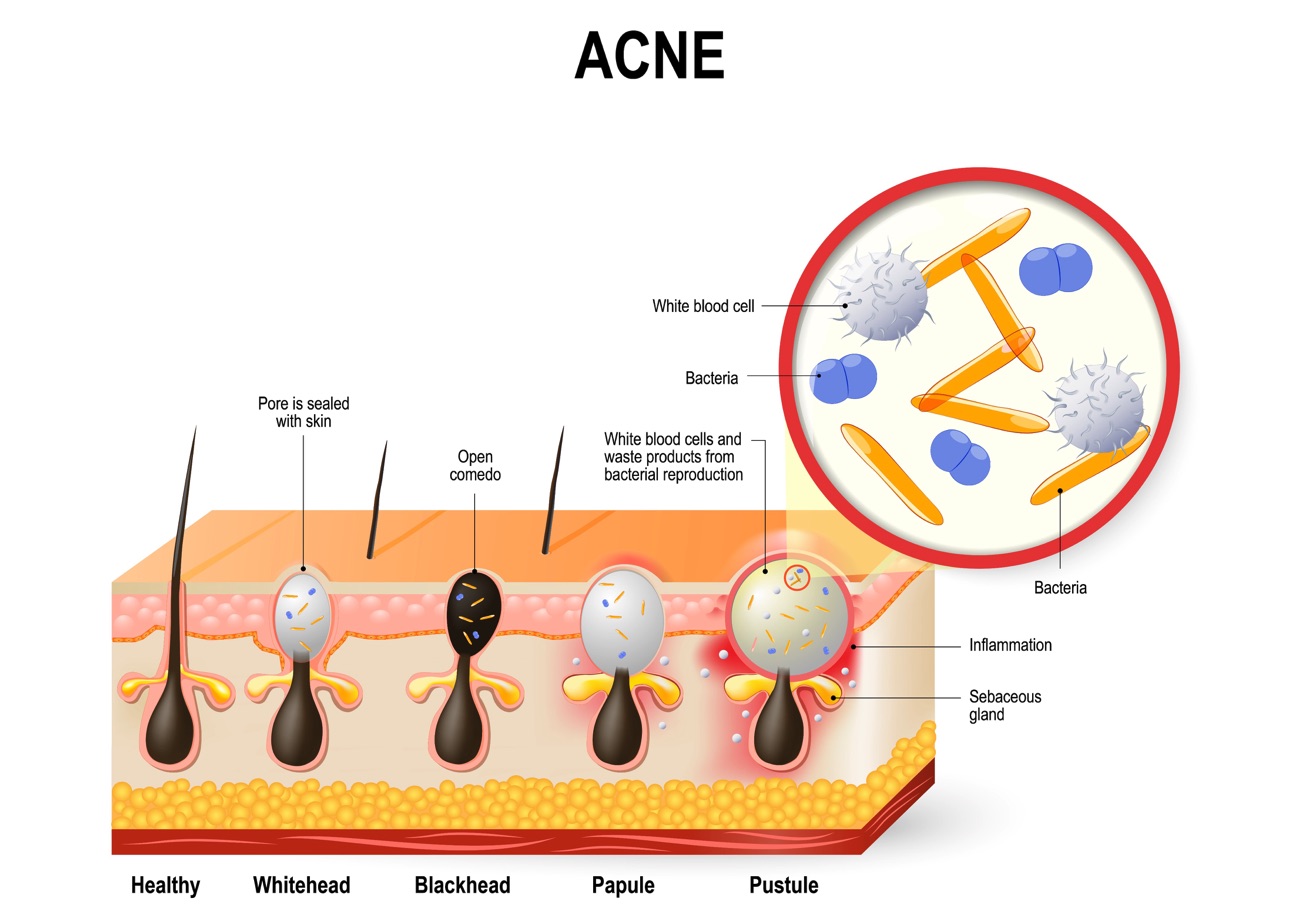
Understanding the Mechanisms: A Closer Look
Acne pathogenesis involves a complex cascade of events, beginning with the formation of a non-inflammatory lesion called a comedone.
- Comedogenesis: This process starts with the overproduction of sebum, leading to the accumulation of oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria within the hair follicle. The follicle becomes blocked, forming a comedone.
- Inflammation: The trapped sebum creates an environment conducive to P. acnes growth. The bacteria release inflammatory mediators, triggering an immune response characterized by redness, swelling, and pus formation.
- Acne Lesions: The inflammatory response results in the formation of various acne lesions, including papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Acne Triggers:
Q: Does eating chocolate cause acne?
A: While chocolate is often blamed for acne, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. However, chocolate contains sugar, which can potentially trigger an inflammatory response, potentially exacerbating existing acne.
Q: Can stress cause acne?
A: Yes, stress can trigger acne by increasing cortisol levels, which can lead to increased sebum production and inflammation.
Q: Does using makeup cause acne?
A: Not all makeup causes acne. However, some makeup products contain comedogenic ingredients that can clog pores and exacerbate acne. Choosing non-comedogenic makeup and regularly cleaning brushes and applicators can help minimize acne risk.
Q: Can certain medications cause acne?
A: Some medications, including corticosteroids, lithium, and certain antibiotics, can cause acne as a side effect.
Tips for Managing Acne:
- Maintain a balanced diet: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sugary drinks and processed foods.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Practice good skincare habits: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser, avoid harsh scrubbing, and use non-comedogenic skincare products.
- Consult a dermatologist: For persistent or severe acne, seek professional advice from a dermatologist who can recommend appropriate treatments.
Conclusion:
Acne is a complex condition influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from hormonal fluctuations to genetics, diet, stress, and environmental influences. Understanding these triggers is crucial for developing personalized strategies for managing acne. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices, maintaining good skincare habits, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can effectively control acne and achieve clearer, healthier skin.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complexities of Acne: Understanding the Triggers and Pathways. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!