A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Topical Products: Promoting Healing and Preventing Complications
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Topical Products: Promoting Healing and Preventing Complications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Topical Products: Promoting Healing and Preventing Complications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Topical Products: Promoting Healing and Preventing Complications
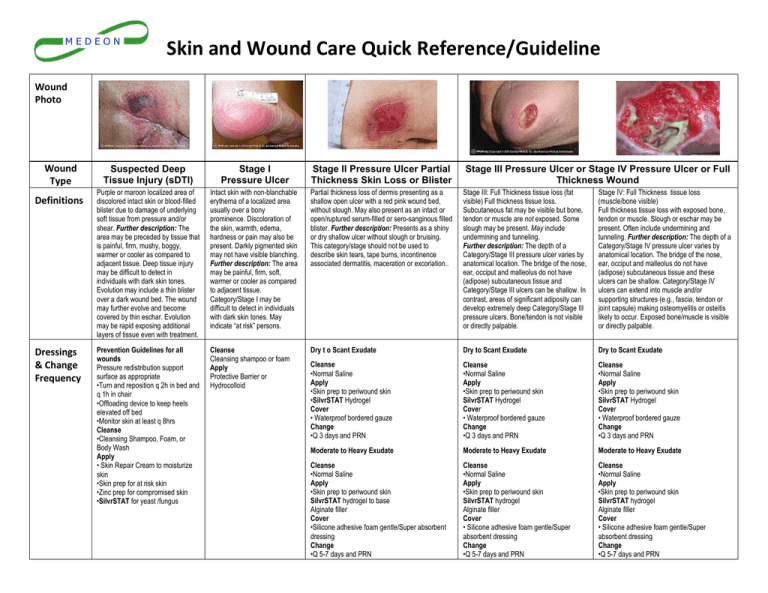
Wound care, a critical aspect of healthcare, involves a multi-faceted approach to manage injuries and promote optimal healing. Topical products, applied directly to the wound site, play a pivotal role in this process, contributing to a range of essential functions. These products, encompassing a diverse array of formulations, act as a crucial bridge between the wound and the surrounding environment, facilitating healing and minimizing complications.
Understanding the Role of Topical Products in Wound Care
Topical products in wound care are not merely surface treatments; they actively engage with the complex biological processes involved in wound healing. Their primary functions include:
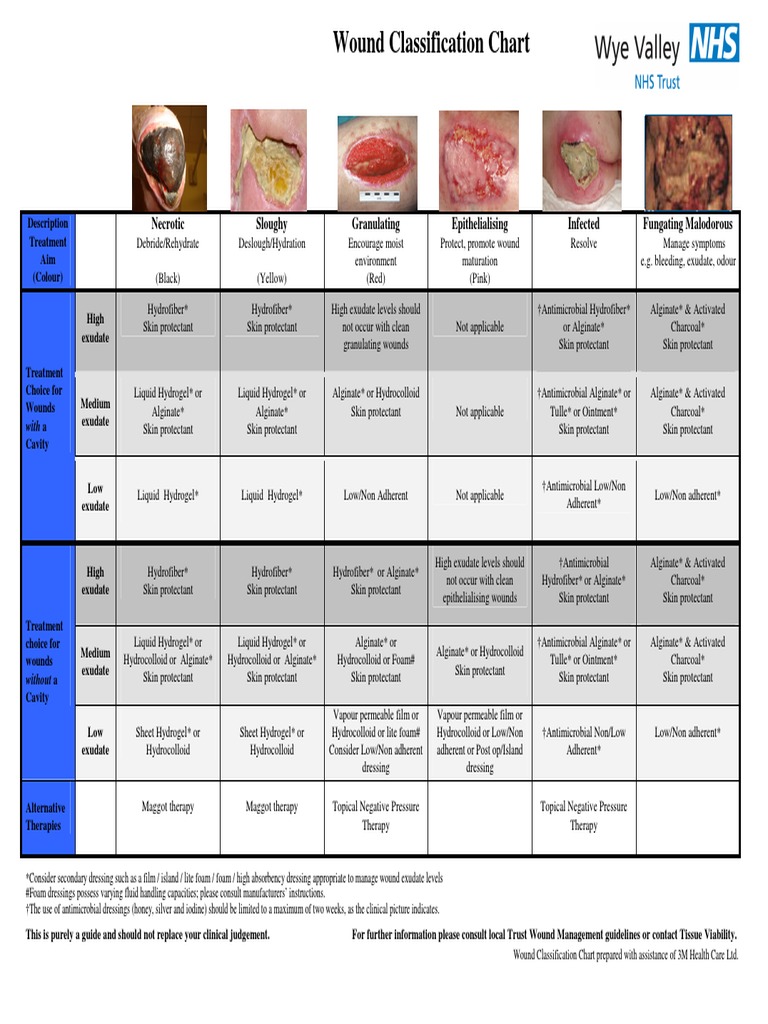
- Debridement: Removing dead tissue, foreign debris, and excess exudate from the wound bed, creating a clean environment conducive to healing.
- Infection Control: Preventing or treating microbial contamination, a significant risk factor for delayed healing and chronic wounds.
- Moisturizing: Maintaining a moist wound environment, crucial for optimal cell proliferation and tissue regeneration.
- Protection: Providing a barrier against external contaminants and mechanical trauma, safeguarding the delicate healing tissues.
- Pain Management: Reducing pain and discomfort associated with the wound, enhancing patient comfort and compliance with treatment.
Types of Topical Products in Wound Care
The spectrum of wound care topical products is vast, each category designed to address specific needs and wound characteristics. Understanding these categories is crucial for selecting the most appropriate product for individual cases.
1. Antiseptics and Disinfectants:
These agents, often containing iodine, chlorhexidine, or hydrogen peroxide, aim to eliminate or inhibit microbial growth, preventing infection and promoting wound healing.
- Iodine-based antiseptics: Widely used for their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, iodine solutions are effective against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. However, they can be cytotoxic to healthy tissue, necessitating careful application.
- Chlorhexidine: Known for its persistent antimicrobial action, chlorhexidine is particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria. Its low toxicity profile makes it suitable for use on open wounds.
- Hydrogen peroxide: While effective against certain bacteria, hydrogen peroxide can damage healthy tissue and delay healing. Its use is generally limited to wound cleansing and debridement.
2. Wound Cleansers:
These products, typically saline solutions or specialized formulations, gently remove debris and exudate without harming the delicate wound bed.
- Normal saline: A versatile and safe option for wound cleansing, saline effectively removes dirt and debris while maintaining the wound’s natural pH balance.
- Specialized cleansers: Formulated with specific ingredients like enzymes or surfactants, these cleansers offer enhanced debridement capabilities, particularly in cases of heavy exudate or necrotic tissue.
3. Antibacterial Agents:
These products, often containing silver or antibiotics, target bacterial infections, preventing their spread and promoting wound healing.
- Silver-containing dressings: Silver ions possess broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, effectively inhibiting bacterial growth while promoting tissue regeneration.
- Antibiotic ointments: These ointments, containing antibiotics like bacitracin or neomycin, are effective against specific bacterial strains. However, their use should be monitored closely to avoid the development of antibiotic resistance.
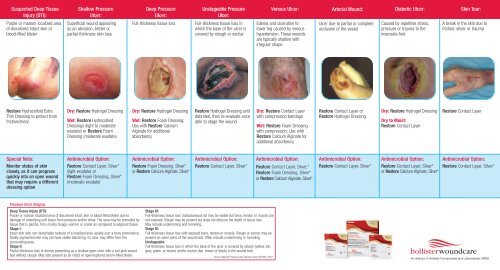
4. Wound Dressings:
These materials, applied directly to the wound, provide a protective barrier, absorb exudate, and facilitate healing.
- Hydrocolloid dressings: These dressings create a moist wound environment, promoting autolytic debridement and accelerating healing. They are often used for partial-thickness wounds and pressure ulcers.
- Hydrogel dressings: Hydrogels provide a cool, soothing effect, rehydrating the wound bed and promoting granulation tissue formation. They are particularly effective for burns and dry wounds.
- Foam dressings: Foam dressings absorb heavy exudate, providing cushioning and protection. They are frequently used for wounds with moderate to high exudate levels.
- Alginate dressings: Alginates are highly absorbent, forming a gel that helps control exudate and promotes wound healing. They are often used for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate.
5. Growth Factors and Biologics:
These advanced products contain growth factors or other biological agents that stimulate cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, accelerating wound healing and promoting tissue repair.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Derived from the patient’s own blood, PRP contains growth factors that promote wound healing and tissue regeneration.
- Fibroblast growth factor (FGF): FGFs stimulate cell proliferation and angiogenesis, promoting wound closure and tissue repair.
- Collagen-based products: Collagen matrices provide a scaffold for cell growth, promoting tissue regeneration and wound closure.
6. Topical Pain Relief Agents:
These products, often containing lidocaine or benzocaine, provide temporary pain relief, enhancing patient comfort and compliance with wound care regimens.
Importance of Topical Products in Wound Care
The use of topical products in wound care is not merely optional; it is essential for achieving optimal outcomes. These products contribute significantly to:
- Accelerated Healing: By providing a conducive environment for tissue regeneration and cell proliferation, topical products promote faster wound closure and minimize healing time.
- Reduced Infection Risk: Antiseptics, disinfectants, and antibacterial agents effectively control microbial contamination, preventing infection and its associated complications.
- Enhanced Comfort: Topical pain relievers and soothing agents minimize discomfort, improving patient compliance and adherence to treatment plans.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Topical products often represent a cost-effective approach to wound care, minimizing the need for more expensive treatments or hospitalizations.
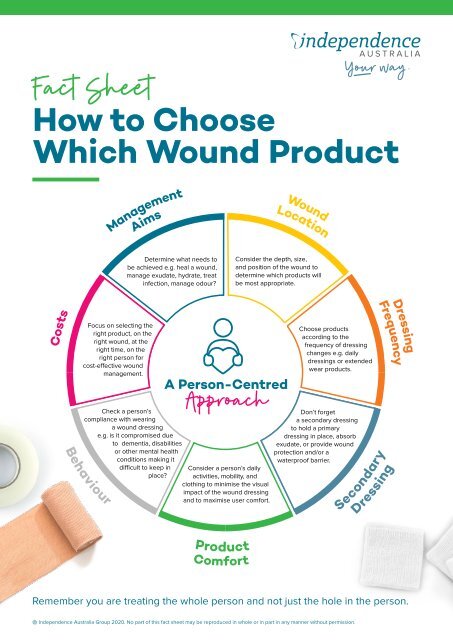
Selecting the Right Topical Product
Choosing the appropriate topical product for a specific wound requires careful consideration of various factors:
- Wound Type: The type of wound (e.g., abrasion, laceration, burn, pressure ulcer) influences the choice of product.
- Wound Severity: The depth and extent of the wound determine the level of care and the specific product needed.
- Exudate Level: The amount of wound drainage dictates the absorbency and type of dressing required.
- Patient Factors: Factors such as age, allergies, and underlying medical conditions influence product selection.
FAQs about Wound Care Topical Products
1. Are topical products safe for all wounds?
While generally safe when used as directed, some products may be unsuitable for certain wound types or individuals. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
2. Can topical products be used on all skin types?
Certain products may be more suitable for specific skin types. For example, individuals with sensitive skin may need hypoallergenic options.
3. How long should I use a topical product?
The duration of use varies depending on the product and the wound. Always follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or your healthcare provider.
4. Can I use multiple topical products at the same time?
Combining different products may lead to adverse reactions or interactions. Consult a healthcare professional before using multiple topical products concurrently.
5. What should I do if I experience an adverse reaction to a topical product?
Discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare professional. They will assess the situation and recommend appropriate action.
Tips for Using Wound Care Topical Products
- Follow Instructions: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for application, frequency, and duration of use.
- Clean Hands: Wash hands thoroughly before and after applying any topical product to prevent contamination.
- Clean Wound: Cleanse the wound gently before applying any product.
- Avoid Overuse: Using excessive amounts of product may not be beneficial and can even be harmful.
- Monitor for Reactions: Observe the wound closely for any signs of adverse reactions, such as redness, swelling, or irritation.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: For any questions or concerns, seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Topical products play a vital role in wound care, promoting healing, preventing complications, and enhancing patient comfort. Understanding the diverse range of products available, their mechanisms of action, and appropriate usage is crucial for effective wound management. By selecting the right product for the specific wound and adhering to proper application techniques, healthcare professionals can optimize healing outcomes and improve patient well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Topical Products: Promoting Healing and Preventing Complications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!