A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice

Wound care is a crucial aspect of nursing practice, encompassing a wide range of skills and knowledge. The use of appropriate wound care products is essential for effective wound management, promoting healing, and preventing complications. This article provides a comprehensive overview of wound care products used in nursing, delving into their classification, application, and significance in achieving optimal patient outcomes.
Understanding the Diverse Landscape of Wound Care Products
Wound care products are categorized based on their primary function, each contributing to specific stages of the healing process.
1. Wound Cleansers:
- Purpose: Wound cleansers are crucial for removing debris, bacteria, and exudate, promoting a clean environment conducive to healing.
-
Types:
- Normal Saline Solution: A sterile, isotonic solution widely used for wound irrigation, particularly in acute wounds.
- Antiseptic Solutions: Solutions like povidone-iodine and chlorhexidine are used to reduce bacterial load in wounds, particularly those with a high risk of infection.
- Enzymatic Debriding Agents: These agents, like collagenase, break down necrotic tissue, facilitating wound cleansing and promoting healing.
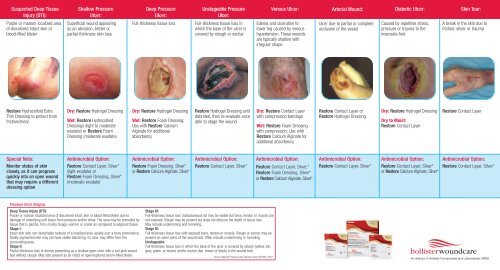
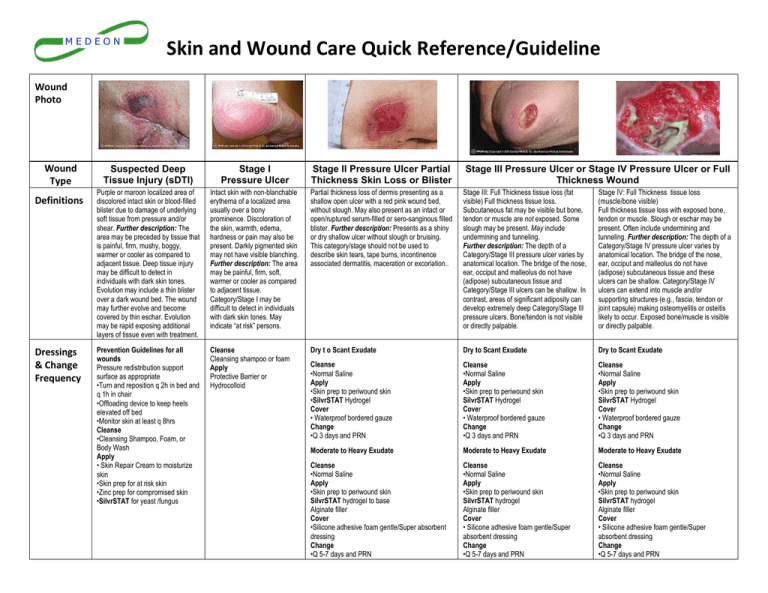
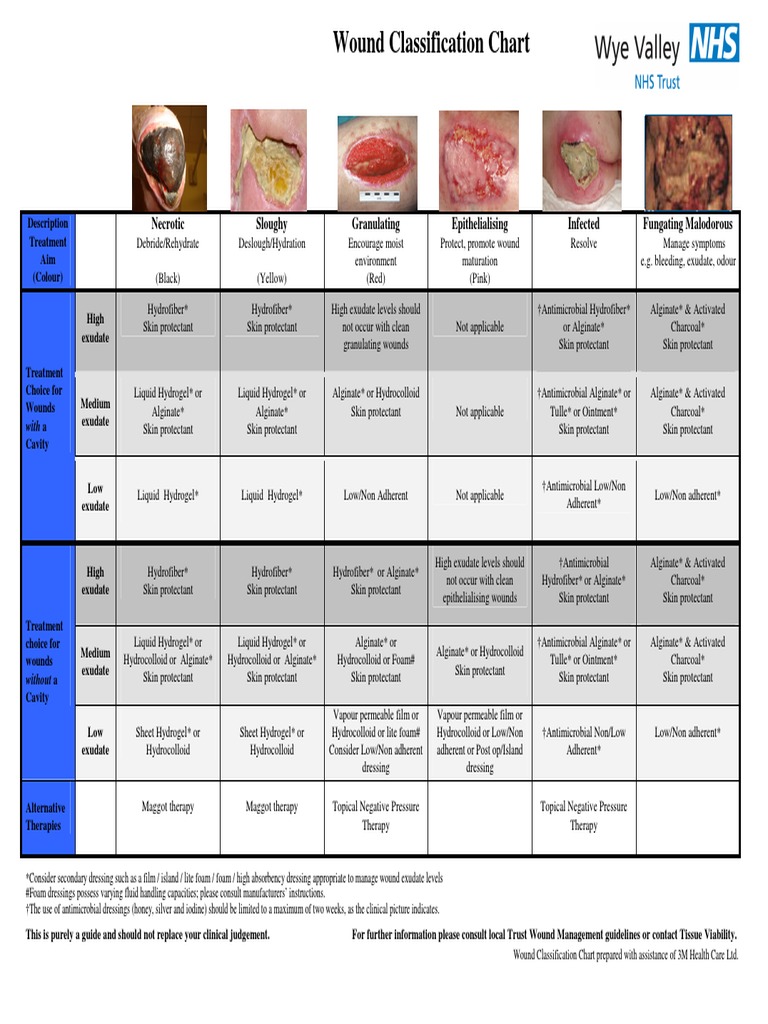
2. Wound Dressings:
- Purpose: Wound dressings serve as a protective barrier, absorbing exudate, and providing a moist environment for healing.
-
Types:
- Gauze Dressings: Versatile and inexpensive, gauze dressings are used for a wide range of wounds, offering absorbency and allowing for visual inspection.
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings create a moist environment, promoting autolytic debridement and minimizing pain during dressing changes.
- Hydrogel Dressings: Hydrogel dressings are ideal for dry or necrotic wounds, providing moisture and facilitating debridement.
- Foam Dressings: Foam dressings offer excellent absorption, cushioning, and insulation, making them suitable for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate.
- Alginate Dressings: Derived from seaweed, alginate dressings are highly absorbent and provide hemostasis, making them suitable for wounds with heavy exudate.
- Silver-Containing Dressings: These dressings possess antimicrobial properties, preventing infection and promoting healing in wounds at risk.
- Transparent Film Dressings: These dressings are semi-permeable, allowing for visual inspection while maintaining a moist environment and protecting the wound.
3. Wound Closure Products:
- Purpose: Wound closure products facilitate wound closure, minimizing scarring and promoting healing.
-
Types:
- Sutures: Sutures are thread-like materials used to close wounds, providing secure closure and promoting healing.
- Staples: Staples are metal fasteners used for wound closure, particularly in skin wounds.
- Adhesive Strips: These strips offer a non-invasive method of wound closure, particularly suitable for superficial wounds.
- Tissue Adhesives: Tissue adhesives are liquid solutions that form a bond over the wound, promoting healing and minimizing scarring.
4. Wound Management Devices:
- Purpose: These devices aid in wound management, promoting healing and preventing complications.
-
Types:
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT involves applying negative pressure to the wound, promoting drainage, granulation tissue formation, and wound closure.
- Wound Vacs: These devices are used in conjunction with NPWT, creating a sealed environment and facilitating wound healing.
- Pulse Lavage Systems: These systems use pressurized saline solution to cleanse wounds, removing debris and promoting healing.
- Skin Staplers: These devices are used for wound closure, particularly in skin wounds, offering a quick and efficient method.
5. Topical Wound Care Products:
- Purpose: These products are applied directly to the wound, promoting healing and preventing complications.
-
Types:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat wound infections, preventing further complications.
- Antiseptics: Antiseptics are used to reduce bacterial load in wounds, promoting healing and preventing infection.
- Moisturizers: Moisturizers help maintain skin integrity, reducing dryness and promoting healing.
- Growth Factors: These products stimulate cell growth and promote wound healing.
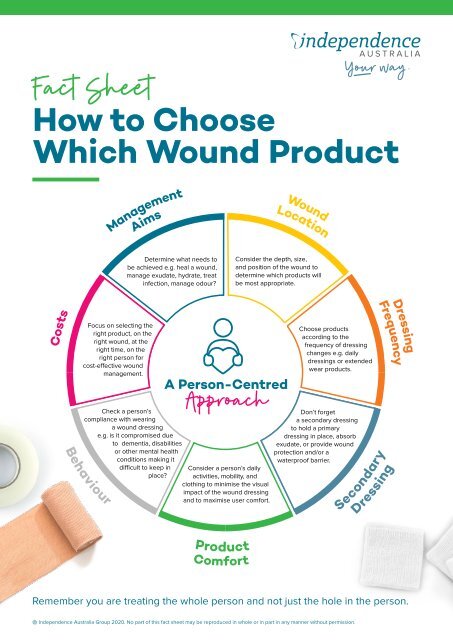
The Importance of Proper Product Selection and Application
Selecting and applying wound care products correctly is crucial for effective wound management. Nurses must consider the following factors:
- Type of wound: The type of wound, including its size, depth, and location, determines the appropriate product selection.
- Wound bed characteristics: Factors like the presence of exudate, granulation tissue, or necrotic tissue influence product choice.
- Patient’s health status: The patient’s overall health, including their age, underlying conditions, and allergies, must be considered.
- Product compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between different products is essential to avoid adverse reactions.
- Application technique: Proper application technique ensures optimal product efficacy and patient comfort.
Benefits of Utilizing Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice
The use of appropriate wound care products offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced wound healing: Products like hydrocolloid dressings and NPWT promote a moist environment, facilitating wound closure and minimizing scarring.
- Reduced infection risk: Antimicrobial dressings and antiseptics effectively control bacterial load, preventing infection and promoting healing.
- Improved patient comfort: Pain management, achieved through products like hydrocolloid dressings and wound cleansers, enhances patient comfort and promotes adherence to treatment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Proper wound care product selection can reduce complications, leading to shorter hospital stays and lower healthcare costs.
FAQs Regarding Wound Care Products in Nursing
1. What are the common complications associated with wound care?
Common complications associated with wound care include infection, delayed healing, dehiscence (wound opening), and excessive scarring.
2. How can nurses prevent wound infections?
Nurses can prevent wound infections by following strict aseptic techniques during wound care, using antimicrobial dressings, and monitoring for signs of infection.
3. What are the key considerations for choosing a wound dressing?
Key considerations for choosing a wound dressing include the type of wound, the amount of exudate, the patient’s health status, and the desired outcome.
4. What are the potential adverse effects of wound care products?
Potential adverse effects of wound care products include allergic reactions, skin irritation, and delayed healing.
5. How can nurses educate patients on proper wound care?
Nurses can educate patients on proper wound care by providing clear and concise instructions, demonstrating the application of products, and answering questions.
Tips for Effective Wound Care Product Utilization
- Follow manufacturer instructions: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for product use, application, and disposal.
- Assess the wound regularly: Regularly assess the wound for signs of infection, healing progress, and any changes in exudate levels.
- Document product use: Maintain detailed documentation of all wound care products used, including the type, quantity, and application technique.
- Provide patient education: Educate patients on proper wound care practices, including dressing changes, signs of infection, and follow-up appointments.
- Collaborate with other healthcare professionals: Collaborate with physicians, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure optimal wound care management.
Conclusion
Wound care products are essential tools in the nursing arsenal, contributing significantly to effective wound management and patient outcomes. By understanding the diverse range of products available, their specific applications, and the importance of proper selection and application, nurses can optimize wound healing, minimize complications, and enhance patient well-being. Continuous professional development and staying abreast of advancements in wound care products ensure that nurses are equipped with the knowledge and skills to provide optimal care for their patients.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products in Nursing Practice. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!