A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Ensuring Optimal Healing
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Ensuring Optimal Healing
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Ensuring Optimal Healing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Ensuring Optimal Healing

Wound care is a crucial aspect of healthcare, encompassing the treatment and management of injuries that disrupt the integrity of the skin and underlying tissues. Effective wound care aims to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. To achieve these goals, a wide array of products are available, each designed to address specific needs and stages of wound healing. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse world of wound care products, providing insights into their functionalities, applications, and significance in facilitating optimal healing outcomes.
Categorizing Wound Care Products
Wound care products can be broadly categorized based on their primary functions:
1. Cleansing and Debridement:
- Antiseptic Solutions: These solutions, such as povidone-iodine, chlorhexidine, and hydrogen peroxide, are used to kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. They are typically applied to wounds before dressing application.
- Wound Cleansers: Gentle cleansers, often saline-based, are employed to remove debris and foreign matter from wounds without causing further damage.
- Debriding Agents: These agents, including enzymatic debriders and surgical debridement, are used to remove dead tissue (necrosis) from wounds, allowing for better healing and reducing the risk of infection.
2. Wound Dressings:
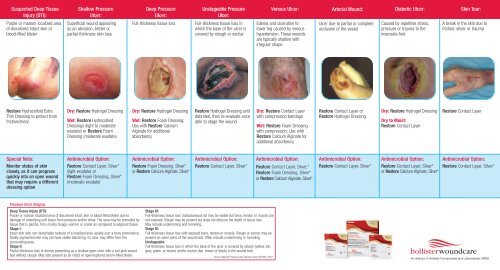
Wound dressings play a vital role in protecting wounds, absorbing exudate, and creating an optimal environment for healing. The choice of dressing depends on the type, size, and stage of the wound.
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings create a moist environment that promotes healing and autolytic debridement. They are suitable for various wounds, including pressure ulcers, burns, and diabetic ulcers.
- Hydrogel Dressings: These dressings hydrate the wound bed, promote granulation tissue formation, and facilitate debridement. They are ideal for dry, necrotic wounds.
- Foam Dressings: These dressings provide absorption of wound exudate, cushioning, and protection. They are commonly used for moderate to heavily exudating wounds.
- Alginate Dressings: These dressings are highly absorbent and form a gel-like substance that helps to control bleeding and promote healing. They are suitable for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate.
- Transparent Films: These dressings are semi-permeable, allowing for gas exchange while providing a barrier against bacteria. They are often used for superficial wounds and for monitoring wound progress.
- Silver-Containing Dressings: These dressings possess antimicrobial properties and are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria. They are particularly useful for wounds at risk of infection.
- Antimicrobial Dressings: These dressings contain antimicrobial agents such as iodine, chlorhexidine, or silver, and are designed to prevent or treat wound infections.
- Vacuum-Assisted Closure (VAC) Therapy: This advanced technology utilizes negative pressure to promote wound healing, reduce edema, and improve tissue perfusion. It is often employed for complex wounds, such as chronic wounds and surgical wounds.
3. Wound Management Products:
- Wound Irrigation Systems: These systems provide a controlled and effective method for cleansing wounds and removing debris.
- Wound Closure Devices: These devices, such as sutures, staples, and adhesive strips, are used to close wounds and promote healing.
- Wound Care Accessories: This category includes various tools and supplies, such as gauze pads, swabs, tape, and bandages, which facilitate wound care procedures.
4. Topical Medications:
- Antibiotics: Topical antibiotics are applied to wounds to prevent or treat bacterial infections.
- Antiseptics: Similar to antiseptic solutions, these topical agents kill bacteria and reduce the risk of infection.
- Growth Factors: These medications stimulate wound healing by promoting cell proliferation and tissue regeneration.
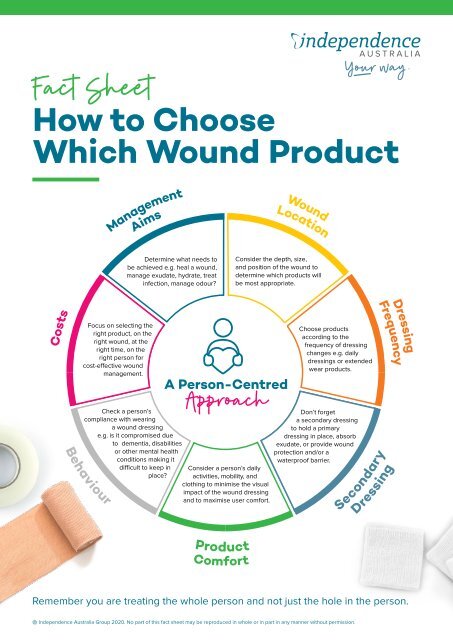
Understanding the Importance of Wound Care Products
The selection and application of appropriate wound care products are paramount to achieving successful wound healing. These products play a crucial role in:
- Preventing Infection: By cleansing wounds, removing debris, and creating a barrier against bacteria, wound care products minimize the risk of infection.
- Promoting Healing: They create an optimal environment for wound healing by providing moisture, debriding necrotic tissue, and stimulating cell growth.
- Managing Exudate: Dressings effectively absorb wound exudate, preventing maceration and promoting a healthy wound bed.
- Protecting the Wound: They provide a protective barrier against further trauma and contamination.
- Minimizing Scarring: Some dressings and topical medications can help to minimize scar formation and improve cosmetic outcomes.
FAQs about Wound Care Products
1. What type of wound dressing is best for me?
The choice of wound dressing depends on the type, size, and stage of the wound, as well as the amount of exudate present. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate dressing for your specific needs.
2. How often should I change my wound dressing?
The frequency of dressing changes varies depending on the type of dressing, the amount of exudate, and the wound’s condition. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the appropriate frequency.
3. Can I use over-the-counter wound care products?
Over-the-counter wound care products are available for minor wounds, but it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for more complex wounds or if infection is suspected.
4. What are the signs of a wound infection?
Signs of a wound infection include increased redness, swelling, pain, warmth, pus discharge, and foul odor. If any of these symptoms occur, seek immediate medical attention.
5. How can I prevent wound infections?
Follow proper wound care instructions, including keeping the wound clean, applying appropriate dressings, and seeking medical attention if necessary.
Tips for Effective Wound Care
- Keep the wound clean: Gently cleanse the wound with saline or a wound cleanser recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Apply appropriate dressings: Choose a dressing that is suitable for the type and stage of the wound.
- Change dressings regularly: Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for dressing changes.
- Monitor the wound: Observe for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, warmth, pus discharge, and foul odor.
- Seek medical attention: If you have concerns about your wound, seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Wound care products play a vital role in facilitating optimal healing outcomes. By understanding the various categories and functionalities of these products, individuals and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions to promote wound healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. Proper selection and application of wound care products, coupled with diligent monitoring and adherence to healthcare recommendations, contribute significantly to positive wound healing experiences.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care Products: Ensuring Optimal Healing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!